HMAC authentication
Function Description
The hmac-auth plugin implements the generation of tamper-proof signatures for HTTP requests based on HMAC algorithm, and uses the signature for identity authentication and authorization.
Configuration Fields
| Name | Data Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
consumers | array of object | Required | - | Configures the caller of the service to authenticate the request. |
date_offset | number | Optional | - | Configures the maximum allowed time deviation of the client, in seconds. It is used to parse the client's UTC time from the Date header of the request, and can be used to prevent replay attacks. If not configured, no validation is performed. |
_rules_ | array of object | Optional | - | Configures the access control list for specific routes or domains, used for authorization of requests. |
The configuration fields for each item in consumers are as follows :
| Name | Data Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
key | string | Required | - | Configures the key extracted from the x-ca-key header of the request. |
secret | string | Required | - | Configures the secret used to generate the signature. |
name | string | Required | - | Configures the name of the consumer. |
The configuration fields for each item in _rules_ are as follows:
| Name | Data Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
_match_route_ | array of string | Optional, either _match_route_ or _match_domain_ must be provided | - | Configures the name of the route to match. |
_match_domain_ | array of string | Optional, either _match_route_ or _match_domain_ must be provided | - | Configures the name of the domain to match. |
allow | array of string | Required | - | Configures the name of the consumer to allow for requests that match the specified route or domain. |
Note:
- If
_rules_is not configured, authentication is enabled for all routes on the current gateway instance by default ; - For requests that pass authentication and authorization, a
X-Mse-Consumerheader will be added to the request headers to identify the name of the consumer.
Configuration Example
The following configuration enables Hmac Auth authentication and authorization for specific routes or domains on the gateway. Note that the key field should not be duplicated.
Enabling for specific routes or domains
consumers:
- key: appKey-example-1
secret: appSecret-example-1
name: consumer-1
- key: appKey-example-2
secret: appSecret-example-2
name: consumer-2
# Configuring Fine-Grained Rules using _rules_ Field
_rules_:
# Rule 1: Matching by route name.
- _match_route_:
- route-a
- route-b
allow:
- consumer-1
# Rule 2: Applies based on domain name matching.
- _match_domain_:
- "*.example.com"
- test.com
allow:
- consumer-2
The allow field under each matching rule specifies the list of callers allowed to access under that matching condition;
In this example, route-a and route-b specified in _match_route_ are the route names filled in when creating the gateway route. When either of these routes is matched, it will allow access to the caller named consumer-1, while denying access to other callers;
In _match_domain_, *.example.com and test.com are used to match the requested domain name. When a match is found, it will allow access to the caller named consumer-2, while denying access to other callers;
Upon successful authentication, the X-Mse-Consumer field will be added to the request header with the value set to the caller's name, such as consumer-1.。
Enable at the Gateway Instance Level
The following configuration enables HMAC authentication at the gateway instance level.
consumers:
- key: appKey-example-1
secret: appSecret-example-1
name: consumer-1
- key: appKey-example-2
secret: appSecret-example-2
name: consumer-2
Description of Signing Mechanism
Configuration Preparation
As mentioned in the guide above, configure the credential settings required for generating and validating signatures in the plugin configuration.
- key: Used for setting in the request header
x-ca-key. - secret: Used for generating the request signature.
Client Signature Generation Method
Overview of the Process
The process for generating a signature on the client side consists of three steps:
Extracting key data from the original request to obtain a string to be signed.
Using encryption algorithms and the configured
secretto encrypt the key data signing string and obtain a signature.Adding all headers related to the signature to the original HTTP request to obtain the final HTTP request.
As shown below :
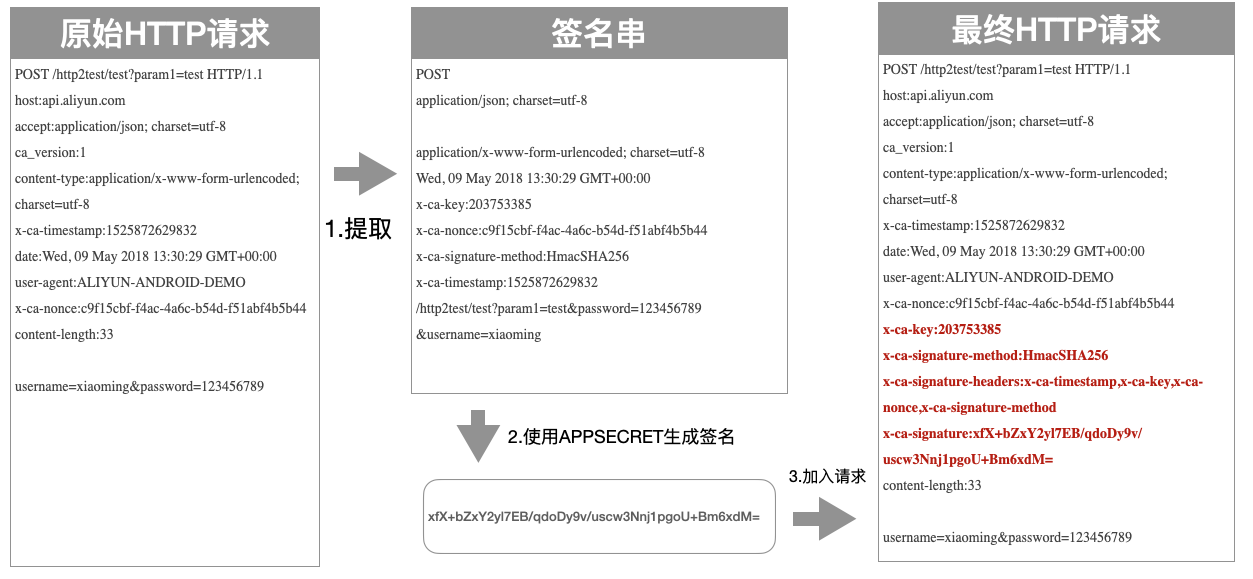
Process for Extracting Signing String
To generate a signature, the client needs to extract key data from the HTTP request and combine it into a signing string. The format of the generated signing string is as follows:
HTTPMethod
Accept
Content-MD5
Content-Type
Date
Headers
PathAndParameters
The signing string consists of the above 7 fields separated by \n. If Headers is empty, no \n is needed. If other fields are empty, the \n should still be retained. The signature is case-sensitive. Below are the rules for extracting each field:
HTTPMethod: The HTTP method used in the request, in all capital letters, such as POST.
Accept: The value of the Accept header in the request, which can be empty. It is recommended to explicitly set the Accept header. When Accept is empty, some HTTP clients will set the default value of
*/*, which may cause signature verification to fail.Content-MD5: The value of the Content-MD5 header in the request, which can be empty. It is only calculated when there is a non-form body in the request. The following is a reference calculation method for Content-MD5 values in :
String content-MD5 = Base64.encodeBase64(MD5(bodyStream.getbytes("UTF-8")));
Content-Type: The value of the Content-Type header in the request, which can be empty.
Date: The value of the Date header in the request. When the
date_offsetconfiguration is not enabled, it can be empty. Otherwise, it will be used for time offset verification.Headers: Users can select specific headers to participate in the signature. There are the following rules for concatenating the signature string with headers:
- The keys of the headers participating in the signature calculation are sorted in alphabetical order and concatenated as follows:
HeaderKey1 + ":" + HeaderValue1 + "\n"\+
HeaderKey2 + ":" + HeaderValue2 + "\n"\+
...
HeaderKeyN + ":" + HeaderValueN + "\n" - If the value of a header is empty, it will participate in the signature with the
HeaderKey+":"+"\n"only, and the key and english colon should be retained. - The set of keys for all headers participating in the signature is separated by a comma and placed in the
X-Ca-Signature-Headers header. - The following headers are not included in the header signature calculation: X-Ca-Signature, X-Ca-Signature-Headers, Accept, Content-MD5, Content-Type, Date.
- The keys of the headers participating in the signature calculation are sorted in alphabetical order and concatenated as follows:
PathAndParameters: This field contains all parameters in the path, query, and form. The specific format is as follows:
Path + "?" + Key1 + "=" + Value1 + "&" + Key2 + "=" + Value2 + ... "&" + KeyN + "=" + ValueN
Notes:
- The keys of the query and form parameter pairs are sorted alphabetically, and the same format as above is used for concatenation.
- If there are no query and form parameters, use the path directly without adding
?. - If the value of a parameter is empty, only the key will be included in the signature. The equal sign should not be included in the signature.
- If there are array parameters in the query or form (parameters with the same key but different values), only the first value should be included in the signature calculation.
Example of Extracting Signing String
The initial HTTP request :
POST /http2test/test?param1=test HTTP/1.1
host:api.aliyun.com
accept:application/json; charset=utf-8
ca_version:1
content-type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8
x-ca-timestamp:1525872629832
date:Wed, 09 May 2018 13:30:29 GMT+00:00
user-agent:ALIYUN-ANDROID-DEMO
x-ca-nonce:c9f15cbf-f4ac-4a6c-b54d-f51abf4b5b44
content-length:33
username=xiaoming&password=123456789
The correct generated signature string is :
POST
application/json; charset=utf-8
application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8
Wed, 09 May 2018 13:30:29 GMT+00:00
x-ca-key:203753385
x-ca-nonce:c9f15cbf-f4ac-4a6c-b54d-f51abf4b5b44
x-ca-signature-method:HmacSHA256
x-ca-timestamp:1525872629832
/http2test/test?param1=test&password=123456789&username=xiaoming
Signature Calculation Process
After extracting the key data from the HTTP request and assembling it into a signature string, the client needs to encrypt and encode the signature string to form the final signature.
The specific encryption format is as follows, where stringToSign is the extracted signature string, secret is the one filled in the plugin configuration, and sign is the final generated signature:
Mac hmacSha256 = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
byte[] secretBytes = secret.getBytes("UTF-8");
hmacSha256.init(new SecretKeySpec(secretBytes, 0, secretBytes.length, "HmacSHA256"));
byte[] result = hmacSha256.doFinal(stringToSign.getBytes("UTF-8"));
String sign = Base64.encodeBase64String(result);
In summary, the stringToSign is decoded using UTF-8 to obtain a Byte array. Then, an encryption algorithm is used to encrypt the Byte array, and finally, the Base64 algorithm is used to encode the encrypted data, resulting in the final signature.
The Process of Adding a Signature
The client needs to include the following four headers in the HTTP request to be transmitted to the API gateway for signature verification:
x-ca-key: The value is the APP Key and is required.
x-ca-signature-method: The signature algorithm, the value can be HmacSHA256 or HmacSHA1, optional. The default value is HmacSHA256.
x-ca-signature-headers: The collection of keys for all signature headers, separated by commas. Optional.
x-ca-signature: The signature and it is required.
Here is an example of a complete HTTP request with a signature :
POST /http2test/test?param1=test HTTP/1.1
host:api.aliyun.com
accept:application/json; charset=utf-8
ca_version:1
content-type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8
x-ca-timestamp:1525872629832
date:Wed, 09 May 2018 13:30:29 GMT+00:00
user-agent:ALIYUN-ANDROID-DEMO
x-ca-nonce:c9f15cbf-f4ac-4a6c-b54d-f51abf4b5b44
x-ca-key:203753385
x-ca-signature-method:HmacSHA256
x-ca-signature-headers:x-ca-timestamp,x-ca-key,x-ca-nonce,x-ca-signature-method
x-ca-signature:xfX+bZxY2yl7EB/qdoDy9v/uscw3Nnj1pgoU+Bm6xdM=
content-length:33
username=xiaoming&password=123456789
Server-side Signature Verification Method
Overview of the Process
The server-side signature verification of the client's request involves four steps :
Extract crucial data from the received request to obtain a string for signing.
Retrieve the
keyfrom the received request and use it to query its correspondingsecret.Encrypt the string for signing using the encryption algorithm and
secret.Retrieve the client's signature from the received request, and compare the consistency of the server-side signature with the client's signature.
As shown below :

Troubleshooting Signature Errors
When the gateway signature verification fails, the server-side signing string (StringToSign) will be returned to the client in the HTTP Response Header. The key is X-Ca-Error-Message. Users only need to compare the locally calculated signing string with the server-side signing string returned to locate the problem;
If the StringToSign on the server side is consistent with that on the client side, please check whether the APP Secret used for signature calculation is correct;
Because line breaks cannot be represented in HTTP headers, all line breaks in the StringToSign are replaced with #, as shown below:
X-Ca-Error-Message: Server StringToSign:`GET#application/json##application/json##X-Ca-Key:200000#X-Ca-Timestamp:1589458000000#/app/v1/config/keys?keys=TEST`
Related Error Codes
| HTTP Status Code | Error Message | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| 401 | Invalid Key | The x-ca-key request header is not provided or is invalid. |
| 401 | Empty Signature | The x-ca-signature request header does not contain a signature. |
| 400 | Invalid Signature | The x-ca-signature request header contains a signature that does not match the server-calculated signature. |
| 400 | Invalid Content-MD5 | The content-md5 request header is incorrect. |
| 400 | Invalid Date | The time offset calculated based on the date request header exceeds the configured date_offset. |
| 413 | Request Body Too Large | The request body exceeds the size limit of 32 MB. |
| 413 | Payload Too Large | The request body exceeds the DownstreamConnectionBufferLimits global configuration. |
| 403 | Unauthorized Consumer | The requesting party does not have access permission. |